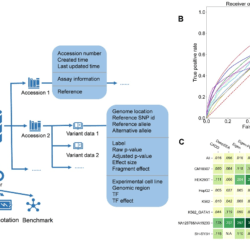
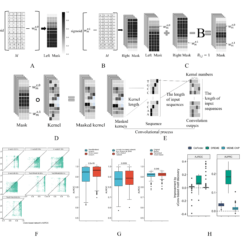
An accurate computational method for cross-platform, multi-modal spatial omics alignment and integration.
Life is an organized arrangement of cells, but any individual cell struggles to function independently once detached from a living organism. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of cell functionality requires considering the microenvironment and spatial location in which cells exist. The rapid development of spatial omics technology greatly facilitates the study of cell function at the Read more about An accurate computational method for cross-platform, multi-modal spatial omics alignment and integration.[…]